A private laboratory specialized in the analysis, testing and failure analysis of materials since 1993
A private laboratory specialized in the analysis, testing and failure analysis of materials since 1993
Definition
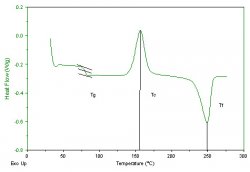
DSC is used to study thermal transitions occurring in a material submitted to a temperature ramp (melting point, glass transition, crystallization…)
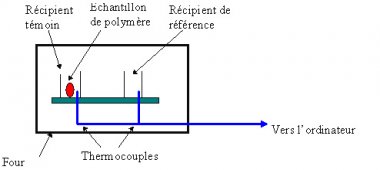
Principle
The DSC analysis consists in measuring the difference in heat flow between the sample and a reference (inert material) when both are submitted to the same temperature ramp. Any transformation occurring in the sample triggers off a heat flow, whereas the reference still be inert. The calorimeter measures the temperature and heat flow, that provides qualitative and quantitative information about physical and chemical transformations within the sample (exothermic or endothermic reactions).
Examples of applications
![]() Polymers identification, raw materials control – melting temperature and transition enthalpy
Polymers identification, raw materials control – melting temperature and transition enthalpy
![]() Degree of crystallinity
Degree of crystallinity
![]() Glass transition, cross-linking and ageing...
Glass transition, cross-linking and ageing...
Equipment
![]() DSC25 TA Instruments
DSC25 TA Instruments
![]() Temperature range : -90°C à +400°C
Temperature range : -90°C à +400°C
![]() Scanning Gas : Nitrogen
Scanning Gas : Nitrogen
![]() temperature accuracy : +/- 0,1°C
temperature accuracy : +/- 0,1°C
![]() Sensibility : 1mW
Sensibility : 1mW