A private laboratory specialized in the analysis, testing and failure analysis of materials since 1993
A private laboratory specialized in the analysis, testing and failure analysis of materials since 1993
Definitions
Particle size: study of the distribution of the size of particles present within samples that are dry (powder, flour, sand, etc.) or liquid (syrups, emulsions, suspensions, etc.)
Laser diffraction granulometry: this technique uses the principle of diffraction and scattering of a laser beam striking a particle.
Principle
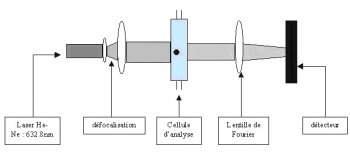
Light from a laser is shone on a cloud of particles, which are suspended in a dispersant (gas or liquid).The particles scatter the light, the larger the particles the smaller the scattering angles. The scattered light is measured by a series of photodetectors placed at different angles. This is known as the diffraction pattern for the sample. The diffraction pattern can be used to measure the size of the particles using Mie or Fraunhofer theory.
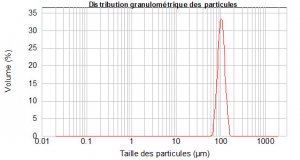
Obtained results allow to draw a curve, called particle size distribution (volumic distribution), and to calculate parameters such as mean diameter, d(0,1), d(0,5), d(0,9)…
Equipment
MASTERSIZER 2000 (Malvern Instruments)
Dispersion units : SCIROCCO 2000 (dry dispersion) and HYDRO 2000SM (liquid dispersion).
| Dispersion | Application | Dispersion unit | Size range | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dry | powders | SCIROCCO 2000 | 200 nm – 2 mm | |||
| liquid | suspensions | HYDRO 2000SM | 20 nm- 2 mm |